How to solve design equation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna
@MicroTalks For one day hands-on workshop. Contact me :- 8072412362 rahulkrish1990@gmail.com This is currently introduced in apj abdul kalam technological university syllabus.
How to solve design equation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna
Introduction to Microstrip Antenna Design
In this section, the speaker introduces the topic of microstrip antenna design and explains the importance of selecting the frequency and substrate material before starting the design process.
Selecting Frequency and Substrate Material
- The first step in designing a microstrip antenna is to choose the frequency for which it will be designed. The frequency selection depends on the application, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- The speaker gives an example of designing an antenna for 5 GHz, which is commonly used for Wi-Fi applications.
- After selecting the frequency, the next step is to choose a suitable substrate material. The availability, cost, and performance parameters of different materials need to be considered.
- FR4 is a commonly used substrate material for microstrip antennas due to its availability and cost-effectiveness.
- Different types of materials like Rogers are also available but are more expensive compared to FR4.
- The relative permittivity (εᵣ) of the chosen substrate material has an impact on antenna performance.
Structure and Dimensions of Microstrip Antenna
This section focuses on explaining the structure and dimensions of a microstrip antenna.
Structure of Microstrip Antenna
- A microstrip antenna consists of three layers: ground layer at the bottom, substrate in between, and patch material on top.
- Copper is commonly used as both patch material and ground layer in microstrip antennas.
- FR4 with a thickness of 1.6 mm is often chosen as the substrate material.
Patch Length and Width Calculation
- To design a rectangular patch microstrip antenna, it is necessary to determine its length (L) and width (W).
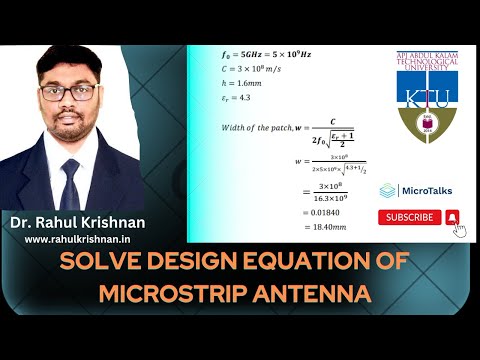
- The width (W) can be calculated using the equation W = c / (2 * f₀ * √(εᵣ + 1/2)), where c is the speed of light, f₀ is the frequency, and εᵣ is the relative permittivity of the substrate material.
- The length (L) of the patch depends on the desired resonant frequency and can be determined using other equations.
Design Equations for Microstrip Antenna
This section covers the design equations used to calculate the width and length of a microstrip antenna patch.
Width Calculation Equation
- The width (W) of a rectangular patch microstrip antenna can be calculated using the equation W = c / (2 * f₀ * √(εᵣ + 1/2)).
- Substituting appropriate values for c, f₀, and εᵣ will give the width in millimeters.
Conclusion
The speaker concludes by summarizing the importance of selecting frequency and substrate material before designing a microstrip antenna. They also mention that further design steps will be covered in subsequent sessions.
Timestamps are approximate and may vary slightly depending on the video playback.
Finding Effective Length and Epsilon Effective
In this section, the speaker explains how to find the effective length (L effective) and epsilon effective (Epsilon effective) for a microstrip patch antenna design.
Finding L Effective
- The equation to find L effective is C divided by 2 F naught root of Epsilon effective.
- C is the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s), F naught is the frequency (5 GHz), and Epsilon effective needs to be determined separately.
Finding Epsilon Effective
- The equation to find Epsilon effective is Epsilon R plus 1/2 plus Epsilon R minus 1/2 multiplied by 1 plus 12 H/W raised to the power of -1/2.
- Epsilon R is the relative permittivity of the substrate, which in this case is FR4 with a value of approximately 4.3.
- H represents the height of the substrate (1.6 mm) and W represents the width of the patch.
Calculating Del L Value
In this section, we learn how to calculate Del L, which represents extension length in a microstrip patch antenna design.
Del L Equation
- Del L = 0.412 H Epsilon effective + 0.3 W/H + 0.265 divided by Epsilon effective - 2 pi 8 W/H + 0.8.
- H is the height of the substrate (1.6 mm), W is the width of the patch, and Epsilon effective was calculated previously.
Determining Substrate Dimensions
This section focuses on determining the length and width of the substrate for the microstrip patch antenna design.
Length of Substrate
- The equation to find the length of the substrate is 6H + L.
- H represents the thickness of the substrate (1.6 mm) and L is the effective length calculated earlier.
Width of Substrate
- The equation to find the width of the substrate is 6H + W.
- W represents the width of the patch, which was determined previously.
Practical Example for 5 GHz Design
In this section, a practical example for designing a microstrip patch antenna at 5 GHz is demonstrated.
Example Parameters
- Frequency (F naught): 5 GHz (converted to Hz)
- Speed of light (C): 3 x 10^8 m/s
- Substrate height (H): 1.6 mm
- Relative permittivity (Epsilon R): 4.3
Calculations
- Using equations mentioned earlier, values for width of patch (W), epsilon effective (Epsilon effective), effective length (L effective), and extension length (Del L) are calculated.
- The dimensions of the substrate can then be determined based on these values.
Summary and Conclusion
This section provides a summary and conclusion about designing a rectangular microstrip patch antenna.
Design Equations Recap
- The design process involves calculating various parameters such as width of patch, epsilon effective, effective length, extension length, and dimensions of the substrate.
- These calculations are based on equations that consider factors like speed of light, frequency, relative permittivity, height, and width.
Timestamps have been associated with relevant sections in accordance with their provided timestamps in order to help others study the transcript effectively.
Calculation of Substrate Length and Width
In this section, the speaker explains how to calculate the length and width of the substrate required for accommodating a patch.
Substrate Length Calculation
- The equation for calculating the length of the substrate is substituted with the values of H (13.93) and L (6) from earlier calculations.
- By substituting these values into the equation, we get a result of 23.5 mm.
- Rounding it off, we can take it as 24 mm as the length of the substrate.
Substrate Width Calculation
- The equation for calculating the width of the substrate is substituted with the values of H (13.93) and W from earlier calculations.
- The result comes out to be around 28 mm.
Patch Dimensions and Design
Here, the speaker discusses the dimensions and design considerations for patches on the microstrip antenna.
- The patch length is approximately 14 mm.
- The patch width is approximately 18 mm.
- For designing purposes, an equation is provided where the substrate has a length of 24 mm and a width of 28 mm.
Final Equation for Antenna Design
This section presents the final equation for designing a microstrip antenna operating at five gigahertz frequency.
- The final equation includes a substrate with a length of 24 mm and a width of 28 mm.
- This design supports a five gigahertz frequency range.
Contact Information
In this section, contact information is provided in case viewers need further assistance or consultation regarding antenna design.
- Viewers can contact the speaker via email at rahulkrrish1990@gmail.com.
- The speaker's phone number is 8072412362.
Timestamps are provided in seconds (s) format.