Los LÓBULOS CEREBRALES, sus funciones, ubicación y características🧠
Los lóbulos cerebrales; explicamos cuáles son, sus funciones, ubicación, y principales características.
Los LÓBULOS CEREBRALES, sus funciones, ubicación y características🧠
Introduction to Lobes of the Brain
In this section, we will learn about the different lobes of the brain and their characteristics. The lobes are symmetrical and divided into two hemispheres - the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere.
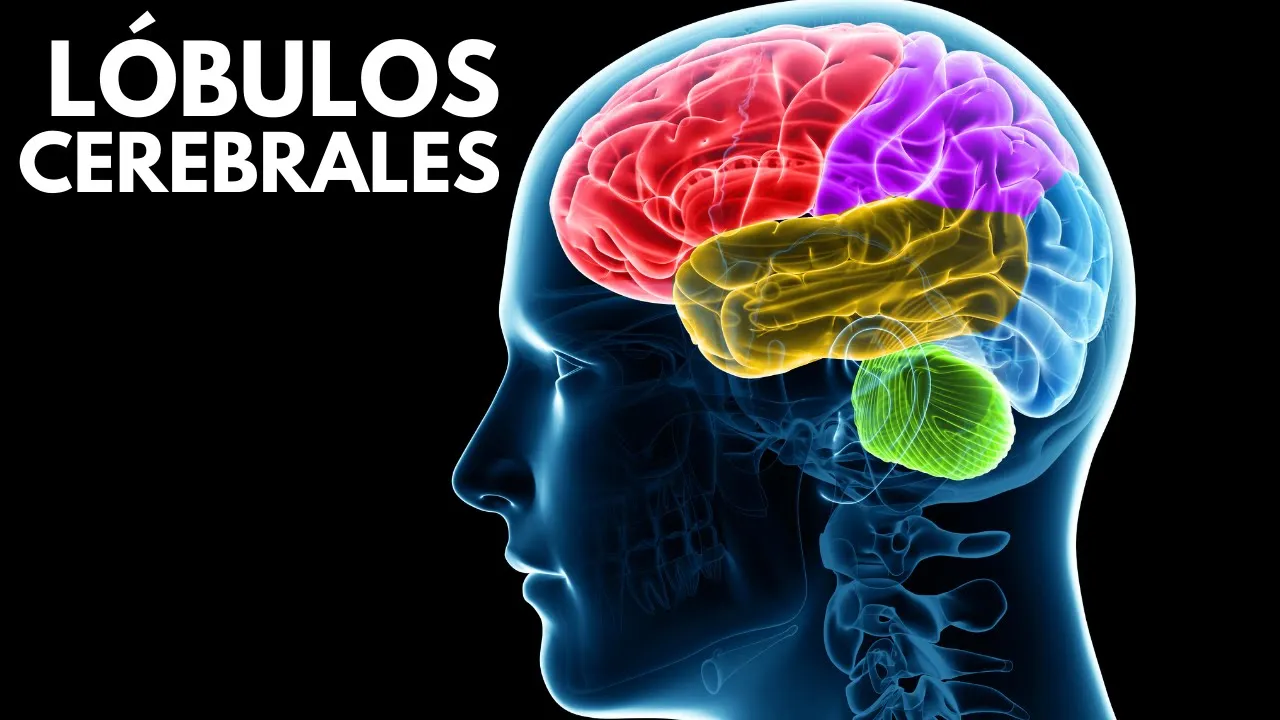
Lobes of the Brain
- The lobes are easily identifiable regions located in the outermost layer of the brain called the cerebral cortex.
- There are four main lobes in each hemisphere of the brain:
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- The frontal lobe is located in the front region of the cortex and is responsible for cognitive functions such as planning, coordination, execution, and behavioral control.
- The temporal lobe plays a role in goal setting, language articulation, emotional regulation, and is considered one of the most evolved regions.
- The parietal lobe processes sensory information from various parts of the body and is involved in tasks like touch, temperature perception, smell, pressure, number recognition, movement control, and visual integration.
- The occipital lobe is responsible for visual processing and perception. It receives visual information from the eyes and transmits it to other brain regions for identification and interpretation.
Functions of Each Lobe
In this section, we will explore specific functions associated with each lobe of the brain.
Frontal Lobe Functions
- The frontal lobe is involved in complex cognitive functions such as intelligence, planning, and coordination of voluntary movements.
- It helps mitigate instinctive and impulsive behavior, contributes to rationality and coherence of conduct.
Parietal Lobe Functions
- The parietal lobe processes sensory information from different body regions, including touch, temperature, smell, and pressure.
- It plays a role in number recognition, movement control, integration of visual information from the occipital lobe.
Temporal Lobe Functions
- The temporal lobe is involved in complex visual activities and facial recognition.
- It plays a crucial role in auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory formation.
Occipital Lobe Functions
- The occipital lobe is responsible for visual perception and receives visual information from the eyes.
- Lesions or disorders in the occipital lobe can lead to vision loss or visual hallucinations.
Conclusion
The lobes of the brain are distinct regions that play vital roles in various cognitive functions. Understanding their functions helps us comprehend how different parts of the brain contribute to our overall perception and behavior.
New Section
This section provides an overview of the insula, its location in the brain, and its functions.
Location and Structure
- The insula is located on the lateral surface of the brain, specifically within the Sylvian fissure, which separates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe. It is a small region at the intersection between the temporal cortex and parietal cortex, situated medially in the brain.
Unique Characteristics
- Unlike other lobes of the brain, the insula is not visible on the external surface of the brain. It is hidden beneath overlapping cortical regions known as opercula.
Functions
- The anterior portion of the insular cortex is closely related to the limbic system and appears to play important roles in subjective emotional experiences and their representation in the body. It has been suggested that this region pairs visceral and emotional states associated with emotional experiences, giving rise to conscious feelings.
- Some research suggests that the insula processes convergent information from ocular globes, generating a genital response in the left hemisphere of the brain. This function allows for emotionally relevant contextualization of sensory experiences.
- Various experiments have demonstrated that the insula plays a role in processing sensory information and contributes to emotional experiences.